Inquiry
Form loading...
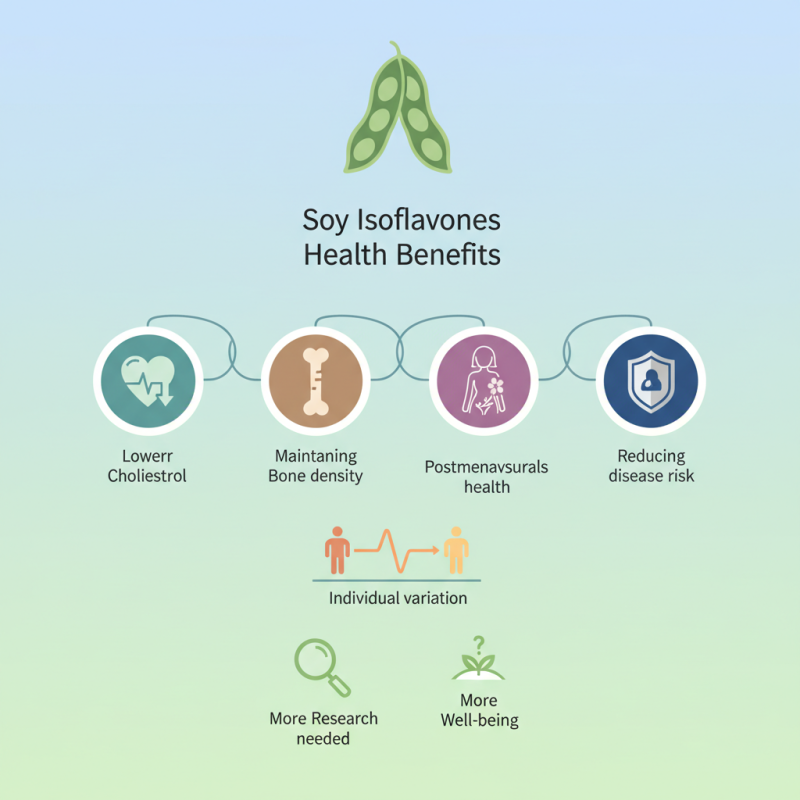
Soy isoflavones are compounds found in soybeans that offer various health benefits. Research suggests they may reduce the risk of certain diseases. These compounds act as phytoestrogens, mimicking estrogen in the body. This property can be beneficial, especially for postmenopausal women.
Some studies indicate that soy isoflavones may lower cholesterol levels. They might also aid in maintaining bone density, which is crucial as we age. Many people overlook the role of diet in health. Including soy isoflavones in meals can be a simple change with significant impact.
However, the effectiveness of soy isoflavones can vary among individuals. Some might experience better results than others. It's essential to consider personal health needs when incorporating them into your diet. Ultimately, soy isoflavones present a promising option for enhancing well-being, but more research is needed.
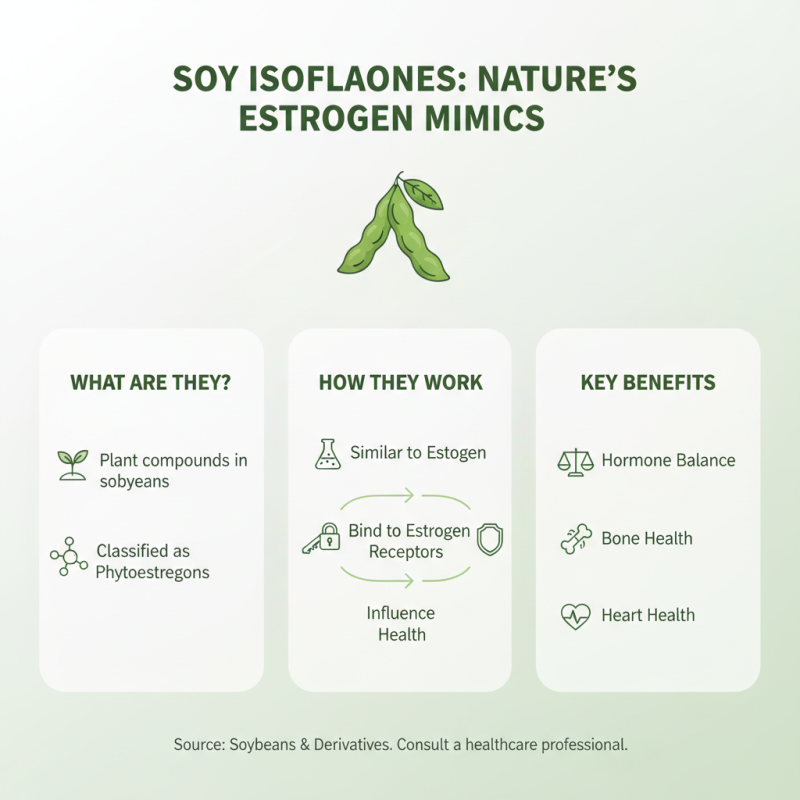
Soy isoflavones are plant compounds found primarily in soybeans. They belong to a class of substances called phytoestrogens, which mimic estrogen in the body. This similarity allows them to interact with estrogen receptors, potentially influencing various health aspects.
Sources of soy isoflavones include tofu, soy milk, tempeh, and edamame. These foods are staples in many cuisines. Incorporating them into meals can enhance nutritional value. However, not everyone tolerates soy well. Some may experience digestive discomfort or allergies.
Understanding these compounds can be complex. Research points to both benefits and risks. Some studies suggest that isoflavones may support heart health and bone density. Yet, their estrogen-like effects can raise questions for certain individuals, especially those with hormone-sensitive conditions. Balancing these factors is vital for informed dietary choices.
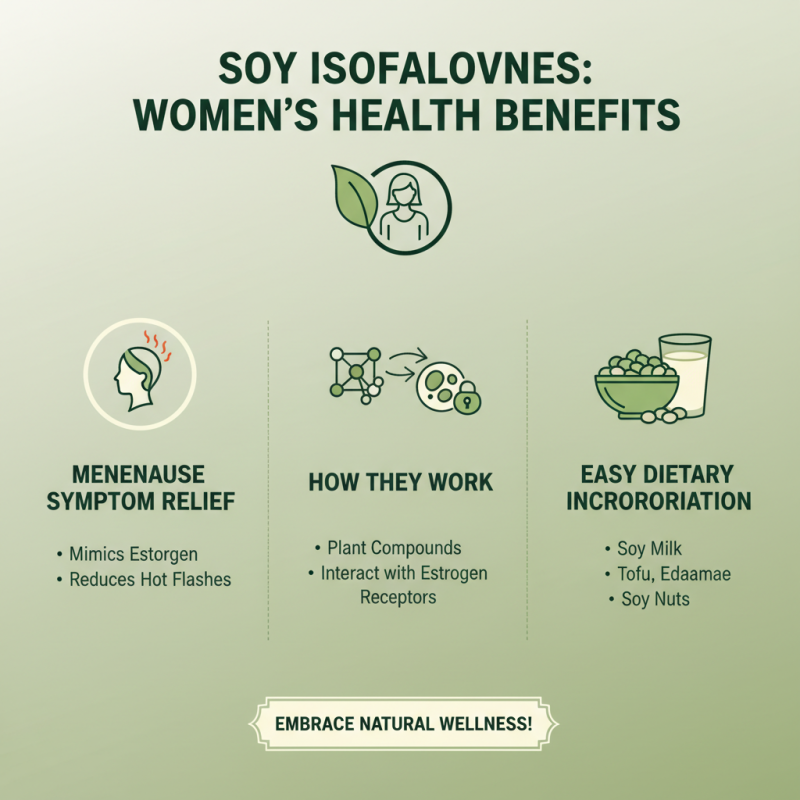
Soy isoflavones have gained attention for their potential health benefits, particularly for women. These plant compounds mimic estrogen, which can help alleviate menopause symptoms. Women experiencing hot flashes may find relief through soy isoflavones. They work by interacting with estrogen receptors in the body. Incorporating soy products into the diet can be an easy way to experience these benefits.
Beyond menopause relief, soy isoflavones may support bone health. Studies suggest that these compounds contribute to bone density maintenance. This is crucial, especially for postmenopausal women at risk of osteoporosis. However, the response to soy isoflavones can vary among individuals. Some may not notice any difference, making it essential to consider personal health goals.
There is growing evidence of the cardiovascular benefits of soy isoflavones. They may help reduce cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Yet, it is worth noting that the research is ongoing. The long-term effects are still being studied. Understanding the nuances of soy isoflavones can empower women to make informed dietary choices.
Soy isoflavones have gained attention for their potential benefits on heart health. These compounds found in soybeans mimic estrogen. This mimicking may help improve cholesterol levels. Research suggests that soy isoflavones can lower LDL cholesterol. They may also raise HDL cholesterol levels, promoting a better cholesterol ratio.
Incorporating soy foods into your diet could boost heart health. Regular consumption might positively impact blood pressure as well. Many individuals find it easy to add tofu, edamame, or soy milk to meals. However, it’s essential to be mindful. Overconsumption may lead to hormonal imbalances in some people. Not everyone's body reacts the same way to soy.
Eating soy isoflavones shows promise, but moderation is key. Listen to your body when trying new dietary changes. The effects may vary from person to person. It's worth considering consultation with a healthcare provider before making any significant changes. Balancing soy intake with other heart-healthy foods might be the best route for overall wellbeing.
Soy isoflavones are natural compounds found in soy products. These compounds have gained attention for their potential role in bone health and osteoporosis prevention. Research suggests that soy isoflavones may mimic estrogen in the body. This is particularly beneficial for postmenopausal women who experience a decline in estrogen levels, leading to increased bone fragility.
Several studies indicate that regular consumption of soy isoflavones can enhance bone density. For instance, women who include soy in their diets often experience less bone loss than those who don’t. However, the exact mechanism remains unclear. Some researchers question how effectively isoflavones can replace estrogen's role.
Incorporating soy foods into your diet might be a smart choice. Tofu, tempeh, and soy milk can be delicious options. But it's important to remember that not everyone's body responds the same way to soy. Some may even experience digestive discomfort. Listening to your body and observing how it reacts is essential.
Soy isoflavones are often praised for their health benefits. However, it's essential to consider potential side effects. Some people may experience mild digestive issues, such as bloating or gas. Others report headaches or mood changes with excessive soy intake.
While isoflavones can support heart health and bone density, moderation is key. Too much soy might interfere with hormone levels. Some studies suggest a link between high soy consumption and thyroid function. Individuals with thyroid issues should watch their intake closely.
Allergic reactions to soy are also possible. Symptoms can range from mild skin rashes to more severe reactions. Pregnant women and those with hormone-sensitive conditions should consult a healthcare provider. The impact of isoflavones varies from person to person. Balancing benefits and risks requires careful thought.






